What Is Hyperpigmentation? Causes, Types and Treatments Explained
Last updated on October 27, 2025
Changes in skin colour are one of the most noticeable shifts people experience over time. Dark patches, sunspots and uneven tone can develop for many different reasons, from years of UV exposure to hormonal fluctuations or even the after-effects of acne. While these areas are not usually harmful, they often raise questions about why the skin responds in this way.
Hyperpigmentation is the term used to describe these darker patches. It can present in several forms, each with its own causes and triggers, and it develops through processes happening deep within the skin. In this article, we’ll explore how hyperpigmentation occurs, the main types to be aware of, what factors increase the likelihood of it developing and the professional and preventive measures that may help manage it.
What is Hyperpigmentation?
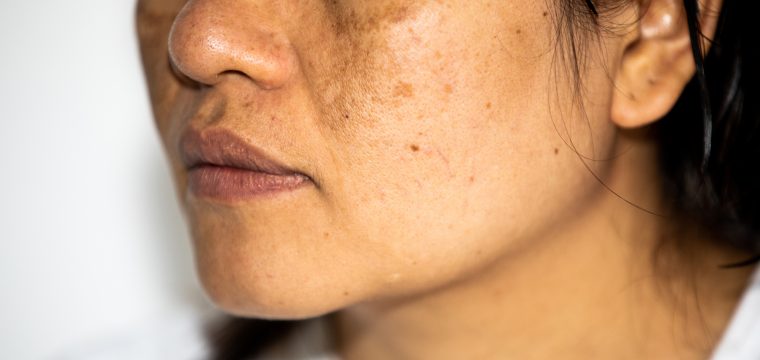
Hyperpigmentation occurs when the skin produces excess melanin, the natural pigment that gives colour to the skin, hair and eyes. This build-up of melanin leads to visible dark patches, spots, or uneven tone. Although pigmentation is a normal protective response against ultraviolet (UV) radiation, when produced unevenly, it can result in localised discolouration.
What is hyperpigmentation? It’s the term for darker areas of skin caused by excess melanin collecting in specific spots.
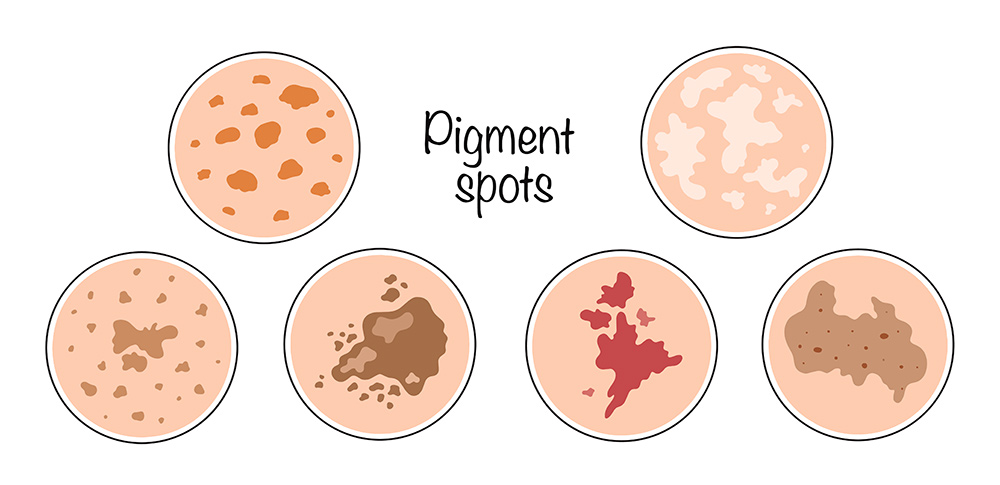
Types of Pigmentation and How They Appear
Different forms of pigmentation show up in distinct ways:
- Sunspots (solar lentigines): Caused by long-term UV exposure, often appearing on the face, hands and arms.
- Melasma: A type of pigmentation often influenced by hormonal changes, usually presenting as symmetrical patches on the face.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH): Dark marks that remain after acne, eczema, or other skin irritation has healed.
- Freckles and other pigment variations: Some are hereditary and become more visible with sun exposure.
Several factors contribute to pigmentation concerns:
- Sun exposure: UV light stimulates melanocytes to produce more melanin.
- Hormonal influences: Pregnancy or certain medications can trigger melasma.
- Skin injury or inflammation: Acne, eczema, or irritation may leave behind dark marks.
- Genetics and skin type: Some people are naturally more prone to pigmentation.
- Age-related changes: Melanin distribution can become less even over time.
- Medications and chemicals: Certain agents may increase pigmentation risk.
How It Develops in the Skin
Pigmentation is controlled by specialised cells called melanocytes. When triggered by sunlight, hormones, or inflammation, these cells produce additional melanin through enzymes such as tyrosinase. This pigment is then transferred to surrounding skin cells, where it accumulates and creates visible discolouration. Superficial pigmentation generally responds more readily to treatment than deeper pigment changes.
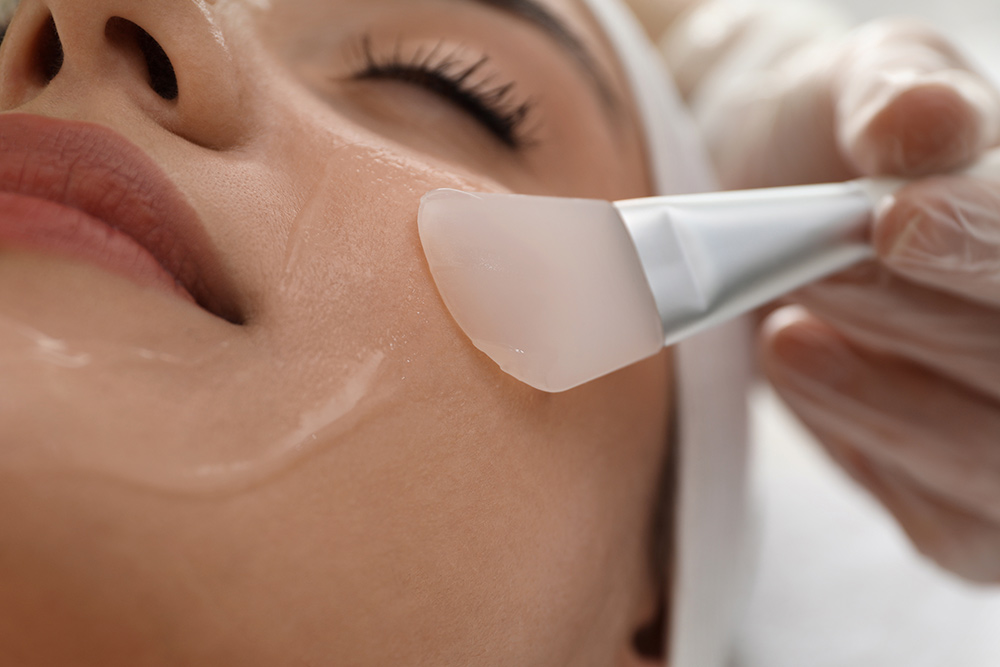
Professional treatments such as peels, resurfacing, or light-based therapies may be used to help manage pigmentation concerns.
When to Seek Professional Advice
Most pigmentation changes are cosmetic, but some require medical review. Seek advice if you notice pigmentation that:
- Appears suddenly or spreads quickly
- Has an irregular shape, boundary or colour
- Occurs in unusual areas of the body
Treatment Options for Hyperpigmentation
Pigmentation can be managed in several ways, depending on its type and cause. Most treatments aim to slow melanin production, remove pigmented cells, or encourage skin turnover.
Options may include:
- Laser and light-based therapies: Target melanin to help break down pigment.
- Resurfacing procedures: Stimulate renewal of the skin’s surface.
- Microneedling techniques: Support regeneration and even tone.
- Chemical peels: Encourage exfoliation and fresh skin growth.
- Topical or oral therapies: topical treatments such as hydroquinone, azelaic acid or kojic acid are good first line options. However, hydroquinone should not be used past 3 months as rebound hyperpigmentation may occur. Oral tranexamic acid may be prescribed to regulate pigment activity.
For more information and details on advanced treatment options, please see our Hyperpigmentation Conditions page.
How to Help Prevent Pigmentation Concerns
Simple steps can help reduce the risk of pigmentation developing or worsening:
- Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen daily.
- Follow a consistent skincare routine with gentle products.
- Avoid picking at blemishes to limit post-inflammatory marks.
- Maintain overall skin health through hydration and balanced nutrition.
Myths and Facts About Pigmentation
There are many misconceptions about pigmentation and how it develops. Clearing up these myths is important, as misunderstanding the condition can lead to ineffective or even harmful approaches to management.
- It always fades on its own: Some pigmentation can linger without intervention.
- It only affects older people: Younger people may also develop pigmentation from acne or sun exposure.
- Sunscreen removes existing spots: Protection helps prevent new pigmentation, but doesn’t clear existing marks.
- Stronger treatments always work faster: Aggressive methods can sometimes worsen pigmentation, especially in sensitive skin types.
Key Points to Remember
Hyperpigmentation occurs when excess melanin causes darker areas of skin to appear. It has different forms, from sunspots to melasma and can be influenced by sun exposure, hormones, inflammation, or genetics. While there are several professional treatment options, prevention through sun protection and consistent skincare remains important.
How to schedule a consultation
To book an appointment, please call us on 02 6059 0612, email us at admin@eclipsehs.com or book online via our website.
Find us here:
13 Yalandra Court
West Albury
NSW 2640
Australia
FAQs
What are the main causes of hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is usually caused by excess sun exposure, hormonal changes, inflammation, or skin injury. Certain medications and genetic factors may also contribute.
How does hyperpigmentation develop in the skin?
It develops when melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells, create more melanin than usual. This pigment collects in specific areas, leading to visible dark patches.
What are the different types of hyperpigmentation?
The most common types include sunspots, melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Each has different triggers and patterns of appearance.
Can hyperpigmentation go away on its own?
Some mild cases may fade over time, especially if sun protection is used consistently. However, many forms can persist without professional treatment.
What’s the difference between hyperpigmentation and melasma?
Melasma is a specific type of hyperpigmentation often linked to hormonal changes, while hyperpigmentation is a broader term covering all pigment conditions. Melasma usually appears as symmetrical patches on the face.
When should you see a doctor about hyperpigmentation?
If pigmentation appears suddenly, changes rapidly, or looks irregular, it should be checked by a medical professional. This helps rule out other underlying conditions.
Is hyperpigmentation permanent or temporary?
Some forms, like post-inflammatory marks, may gradually fade, while others, such as melasma, can be longer-lasting. The outcome depends on the type, depth and cause.
How does sun exposure affect hyperpigmentation?
UV radiation stimulates melanin production, which can darken existing pigmentation and trigger new spots. Consistent sun protection is key to minimising these effects.
Can skincare products reduce hyperpigmentation?
Certain topical agents, such as vitamin C, retinoids, or niacinamide, may help improve uneven tone. Results vary depending on the cause and depth of the pigmentation.
What helps prevent hyperpigmentation from getting worse?
Daily sunscreen use, avoiding skin irritation and following a gentle skincare routine can reduce the risk of worsening pigmentation. Professional advice may help tailor prevention strategies to individual needs.